How image processing and the intelligent edge are transforming operations and adding value across key industries
Humans are highly visual creatures. We gather the vast majority of information about our environments, our daily tasks and each other through visual perception. In fact, sight is so critical to our experience that nearly half the human brain is directly or indirectly involved in visual processing.
As a result, much of the world we’ve created for ourselves — the work we do and the obstacles we face — depends on some form of visual input. As we increasingly look to Artificial Intelligence (AI) to help solve a range of real-world challenges, this means computer vision will, by necessity, have a significant role to play.
What is computer vision?
In the simplest terms, Computer Vision (CV) refers to the use of machine learning to analyze, understand and respond to digital images or videos.
Applying deep learning algorithms to input from cameras allows visual information to be converted into data that can be processed and evaluated for patterns. By analyzing a selection of images, neural networks can be trained to recognize, classify and react to what they “see.”
But computers don’t learn to identify objects the same way humans do. Our broad intelligence means we’re able to use a wide range of attributes, as well as other senses, to identify, characterize and make inferences about many observations at once. We easily adapt our understandings to accommodate variations in size, angle, shape or color.
While computer vision can be trained to solve almost any visual problem, each model is extremely narrow in its capabilities. It’s only able to recognize what it’s been taught to recognize.
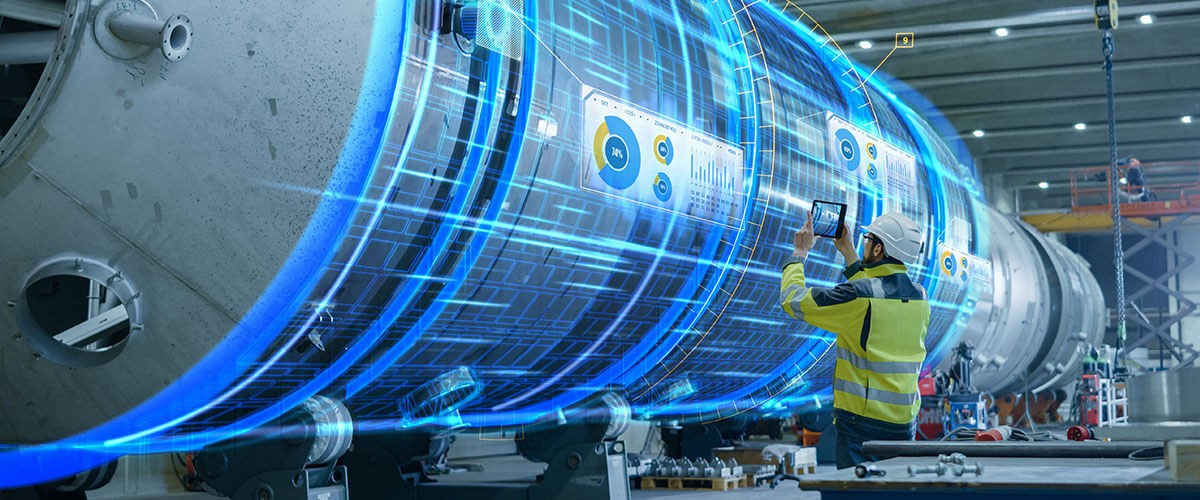
One of the most complex examples of computer vision comes from self-driving cars. Although the capabilities of autonomous vehicles may seem broad, they rely on hundreds or thousands of CV models, non-CV models and higher-level machine learning models working together. The system as a whole is capable of identifying, locating and responding to street signs, traffic lights, pedestrians and other vehicles on the road — but each function requires a specialized algorithm, fine-tuned to that task.
This narrow functionality makes computer vision extremely effective at addressing individual challenges. It also means CV models need to be carefully developed, trained and implemented with a specialized function in mind.